



Palestine is a geographically diverse region located in the Middle East, bordered by Israel to the west, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the southwest, and Lebanon to the north. The region covers an area of approximately 6,000 square miles and has a population of over 4 million people.
The history of Palestine dates back to ancient times, with evidence of human settlement dating back to the Neolithic period. The region was later inhabited by various civilizations, including the Canaanites, Phoenicians, and Hebrews. In the Hellenistic period, Palestine was ruled by the Seleucid Empire and then the Ptolemaic Empire.
In 63 BCE, the region became part of the Roman Empire, and during this time, Christianity emerged as a major religion. After the collapse of the Roman Empire, Palestine was ruled by the Byzantine Empire until the Arab-Muslim conquest in the 7th century.
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Palestine was under Ottoman rule until the British took control during World War I. In 1917, the British issued the Balfour Declaration, which promised to establish a national home for the Jewish people in Palestine.
After World War II, the United Nations proposed a partition plan for Palestine, which led to the establishment of the state of Israel in 1948. This resulted in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians, who became refugees in neighboring countries.
Since then, Palestine has been embroiled in ongoing conflict with Israel, with both sides claiming historical and religious ties to the land. Today, Palestine is divided into two territories: the West Bank, which is occupied by Israel, and the Gaza Strip, which is controlled by the Hamas militant group.
Despite its troubled history, Palestine remains a culturally rich region with a strong sense of identity and resilience. Its people continue to fight for their rights and seek a peaceful resolution to the ongoing conflict.

Palestine is a country that boasts a rich history in agriculture, and the cultivation of bay leaves (Laurus nobilis) is one of its notable agricultural practices. Bay leaves are valued for their distinct flavor and aroma, which make them a popular seasoning in various cuisines around the world. In Palestine, these trees are typically grown in the West Bank, particularly in the Nablus region, where the fertile soil and favorable climate conditions provide an ideal environment for their growth.
The cultivation process begins with the selection of suitable land, followed by the preparation of the soil through plowing and the addition of organic matter to enhance fertility. Bay trees are propagated through seed sowing or by grafting cuttings onto rootstocks. Once planted, the trees require regular watering, weeding, and protection from pests and diseases.
As the trees mature, usually within a few years, the leaves can be harvested. The harvesting process involves carefully selecting the leaves at the right stage of maturity to ensure optimal flavor and potency. After harvesting, the leaves are often dried in the sun or using specialized drying equipment to preserve their qualities.
In Palestine, bay leaves are not only used locally but also exported internationally, contributing to the country's economy. They are often sold whole, ground into powder, or made into essential oils, depending on the market demand.
The Palestinian bay leaf cultivation plays a significant role in the country's agricultural sector, providing employment opportunities and supporting local communities. Additionally, it reflects the traditional knowledge and expertise passed down through generations of Palestinian farmers.
Overall, the cultivation of bay leaves in Palestine is an important aspect of the country's agricultural heritage, contributing to both its cultural identity and economic well-being.
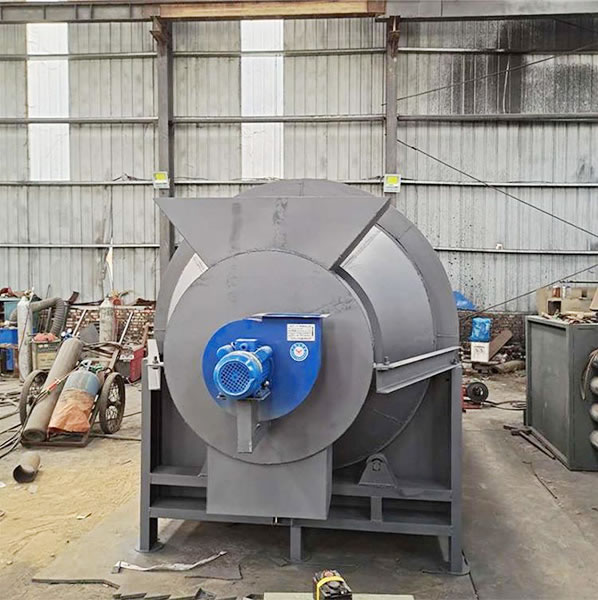

Title: Performance Characteristics of Small Grains Dryer and Its Role in the Deep Processing of Palestinian Zong Leaves
Abstract:
The present study elucidates the performance characteristics of a small grains dryer and its pivotal role in enhancing the value chain of Palestinian zong leaves through deep processing. The analysis delineates the efficiency, precision, and adaptability of the dryer technology in meeting the specific requirements of zong leaf preservation and preparation.
1. Introduction
Palestine holds a rich agricultural heritage, where zong leaves play a significant role as a traditional ingredient. The deep processing of these leaves requires meticulous drying to preserve their nutritional and flavor profiles. A small grains dryer, designed for optimal performance in such applications, has been instrumental in this process.
2. Performance Characteristics of Small Grains Dryer
The small grains dryer boasts several performance features that make it suitable for the task at hand. These include:
a. Efficiency: The dryer operates on advanced thermal principles to ensure rapid moisture removal without compromising the quality of the leaves.
b. Uniformity: It ensures an even distribution of heat, leading to consistent drying results across different batches of zong leaves.
c. Controllability: The dryer's control system allows precise regulation of temperature and humidity levels, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the leaves' natural properties.
d. Energy-Efficiency: Optimized energy consumption is achieved through innovative design, making the process economically viable for large-scale operations.
e. Versatility: The equipment can be adapted to various drying needs, including different types of grains and agricultural products.
3. Role in Palestinian Zong Leaves Deep Processing
The small grains dryer plays a multifaceted role in the deep processing of Palestinian zong leaves:
a. Preservation: By efficiently removing moisture, the risk of microbial growth and spoilage is significantly reduced, extending the shelf life of the product.
b. Quality Maintenance: Gentle drying ensures that the leaves retain their essential oils and nutrients, preserving their aroma and health benefits.
c. Scalability: The technology supports scaling up production without sacrificing the quality of the final product, aiding in meeting market demands.
d. Innovation: The application of this advanced drying technology opens avenues for product innovation, such as creating value-added zong leaf powders or extracts.
4. Conclusion
The integration of a small grains dryer into the Palestinian zong leaf industry represents a significant step forward in deep processing capabilities. Its performance characteristics not only enhance the quality and safety of the product but also pave the way for increased productivity and commercial opportunities. As such, the technology serves as a catalyst for economic growth within the sector while preserving the cultural significance of zong leaves for future generations.
Keywords: Small Grains Dryer, Palestinian Zong Leaves, Deep Processing, Performance Characteristics, Agricultural Innovation.
As the country's requirements for environmental protection and energy efficiency continue to rise, future deep processing of zongye will pay more attention to process innovation and environmental protection energy saving. The emergence of new equipment such as Small grains dryer undoubtedly brings new development opportunities for the deep processing of zongye in Palestine. Entrepreneurs create great achievements, strive to be the first to create brilliance! Create the future of agriculture, hand in hand, build dreams for the future, Jushang drying equipment blesses Palestinian Small grains dryer customers: continue to work hard, show your skills, and leave a brilliant mark on the road of your career!