



The development of agricultural and sideline products in Tanzania has been progressing steadily over the years. The country's diverse climate and fertile land have made it possible to cultivate a wide range of crops, including coffee, cotton, cashew nuts, sisal, and tobacco. These commodities are major contributors to the Tanzanian economy and export market.
Coffee is one of Tanzania's main cash crops, with production centered around the highlands where the climate is suitable for growing Arabica coffee. The quality of Tanzanian coffee is well-regarded internationally, and its export has been a significant source of foreign exchange earnings.
Cotton is another important crop, primarily grown in the southern and central regions of the country. The textile industry in Tanzania relies heavily on locally produced cotton, and efforts have been made to increase productivity through improved farming techniques and the introduction of high-yielding varieties.
Cashew nuts have gained prominence as an export crop, with the majority of production coming from smallholder farmers in various regions. The cashew industry provides employment and income to many households and has become a focal point for rural development initiatives.
Sisal, which is used to make fibers for rope and other products, was once a major export crop in Tanzania. Although its importance has diminished due to synthetic alternatives, sisal remains a valuable source of income for some farmers.
Tobacco is also cultivated in specific regions of Tanzania and is processed into cigarettes, cigars, and other products for both domestic consumption and export. However, due to health concerns and regulatory changes globally, the future of tobacco production may be limited.
In addition to these key crops, Tanzania also produces a variety of other agricultural products such as tea, maize, beans, rice, and fruits like bananas and mangoes. These contribute to food security within the country and sometimes find their way into international markets as well.
The government and several non-governmental organizations (NGOs) have implemented various programs to support the development of agriculture and improve the livelihoods of smallholder farmers. Initiatives include providing access to better seeds, fertilizers, irrigation, and training in modern agricultural practices. These efforts aim to enhance productivity, diversify crop options, and ultimately boost the sector's contribution to the Tanzanian economy.

In Tanzania, the apple deep processing industry has witnessed some growth in recent years. Several companies have emerged to capitalize on the potential of this sector, offering various products ranging from apple juice to jams, syrups, and even cider.
The majority of these enterprises are located in the central and northern regions of the country where apples are grown in abundance. These companies employ a combination of traditional and modern techniques to ensure the highest quality of their end products. They often use advanced equipment for sorting, washing, and packaging the apples to meet international standards.
The local demand for apple products is steadily increasing, with consumers becoming more health-conscious and appreciating the nutritional value that apples provide. This domestic market is further complemented by export opportunities, as many of Tanzania's apple products have found their way into regional markets and beyond.
Government initiatives and investment incentives have been crucial in fostering the development of this industry. The government provides support through infrastructure improvements, training programs, and access to finance, which has helped small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) enter the market.
As environmental sustainability becomes a priority globally, several apple processing businesses in Tanzania have adopted eco-friendly practices such as using renewable energy sources and implementing recycling programs to reduce waste.
The challenges faced by these enterprises include maintaining consistent quality, managing post-harvest losses, and competing with imported apple products due to lower production costs in other countries. Despite these obstacles, the outlook for the apple deep processing industry in Tanzania remains promising, with innovation and strategic partnerships playing key roles in its future growth.
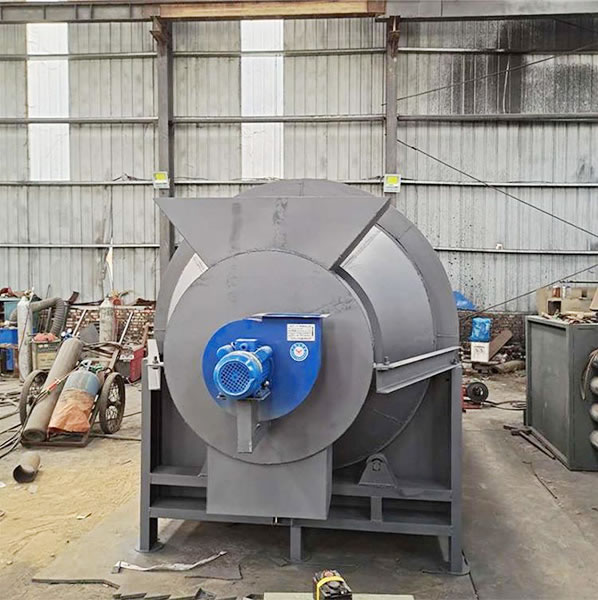

A small dryer plays a crucial role in the apple deep processing industry. It effectively removes moisture from the fruit, making it suitable for various products such as dried apples, juices, and cider. By using a dryer, processors can maintain product quality and extend shelf life, ensuring the safety and nutritional value of the end product.
As national requirements for environmental protection and energy efficiency continue to rise, the future of apple deep processing will place greater emphasis on process innovation and eco-friendly energy conservation. The emergence of new equipment such as small dryers undoubtedly brings new development opportunities for Tanzania's apple deep processing industry. Hard work is rewarded by heaven, virtue by earth, sincerity by people, trustworthiness by business, and excellence by profession. For rural revitalization, let us join hands, build dreams for the future, and Jushang drying equipment extends its blessings to Tanzanian small dryer customers: may you have peace and joy, and all your wishes come true. May you be happy year after year and victorious year after year!